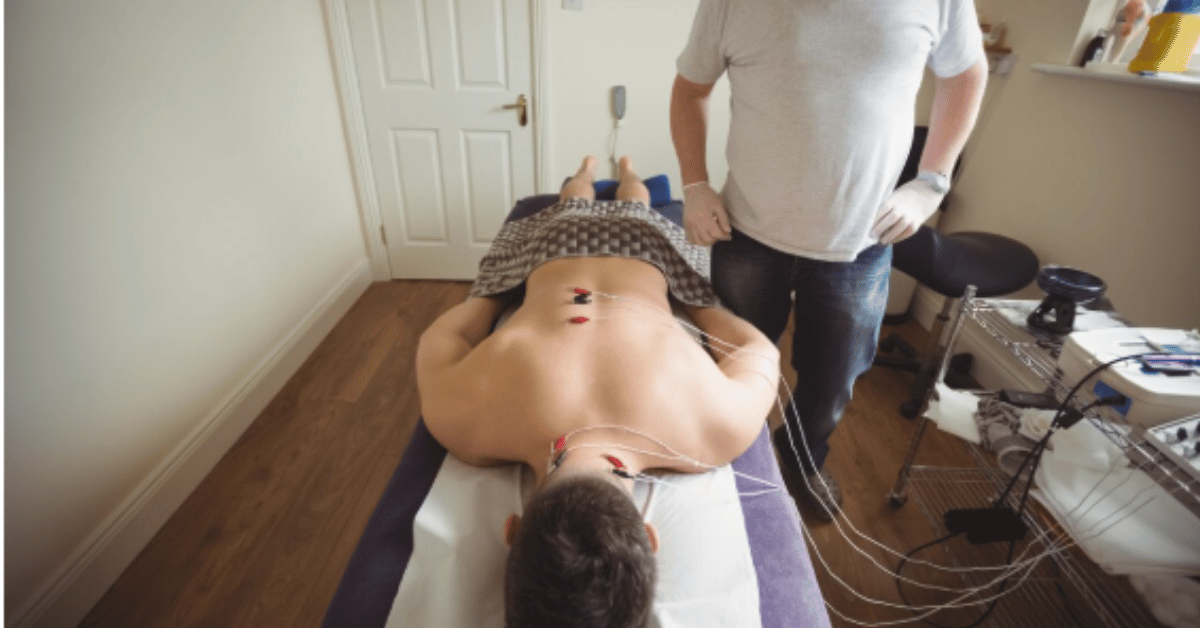
Pulsierende Signal Therapie, often translated as Pulsed Signal Therapy, is a therapeutic method designed to restore cellular communication and enhance natural healing processes in the body. Within the first few sessions, many patients report reduced discomfort, improved mobility, and better circulation. At its core, the therapy works by delivering precise electromagnetic signals that mimic natural biological rhythms, encouraging damaged tissues and cells to resume optimal function. Searchers curious about this treatment usually want to know how it works, who can benefit, and whether it is supported by credible research. To answer that intent directly: Pulsierende Signal Therapie is used in orthopedic recovery, chronic pain relief, joint rehabilitation, and even sports medicine, offering a non-invasive path to recovery where conventional methods sometimes fall short.
The therapy has roots in biophysics, where scientists observed that cells respond not only to chemical signals but also to electromagnetic ones. By translating this principle into medical practice, pulsierende Signal Therapie aims to “remind” cells of their natural rhythm and functionality. Advocates believe this technology has potential to complement traditional medicine while reducing dependency on invasive procedures or long-term pharmaceutical regimens. To understand its significance, one must explore its scientific foundations, patient applications, controversies, and emerging possibilities in healthcare. This article provides a full exploration of its mechanics, benefits, challenges, and future outlook, with clear examples and professional insights to help readers grasp both the promise and limitations of this innovative therapy.
The Scientific Foundation of Pulsierende Signal Therapie
The principle behind pulsierende Signal Therapie lies in the concept that cells communicate using electrical signals. When injuries occur or chronic conditions develop, these signals may weaken or become irregular. By applying pulsed electromagnetic fields, the therapy provides an external stimulus that resonates with the body’s own bioelectric frequencies. Unlike continuous waves, pulsed signals are more biologically compatible because they prevent overstimulation and instead synchronize with natural cell cycles. Research in cellular biology shows that mitochondria, the energy centers of cells, respond favorably to such stimuli, leading to increased ATP production, which is vital for energy and repair. This scientific underpinning explains why patients often experience both short-term relief and long-term improvement in tissue health.
Historical Development and Medical Integration
The roots of pulsierende Signal Therapie can be traced back to mid-20th-century studies in Eastern Europe, where early prototypes were tested for bone healing. These experiments revealed faster recovery times compared to patients without stimulation. Over decades, the method evolved, particularly in Germany and Switzerland, where medical engineers refined the technology into safe, clinically adaptable devices. By the 1990s, orthopedic clinics began integrating it into rehabilitation protocols for knee injuries, fractures, and post-surgical recovery. Today, it is not uncommon to see physiotherapists pairing it with manual therapy or exercise regimens to maximize results. In many clinics, its adoption symbolizes a shift toward integrative medicine, blending technology with natural healing principles.
How Pulsierende Signal Therapie Works in Practice
A typical session involves a patient sitting or lying near a specialized device that emits low-frequency electromagnetic pulses. These pulses are carefully calibrated in both intensity and frequency to match the condition being treated. For joint pain, for example, lower intensities may be applied for longer durations, while bone healing might require more focused, higher-intensity settings. The therapy is painless, often described as a gentle tapping or warmth, and sessions usually last between 20 to 40 minutes. Practitioners emphasize the importance of consistency, recommending multiple sessions per week during acute recovery phases. Patients appreciate its non-invasive nature, especially compared to injections or surgeries, and its absence of significant side effects enhances its appeal across diverse age groups.
Key Benefits Reported by Patients
Patients undergoing pulsierende Signal Therapie frequently report improvements that extend beyond pain reduction. Enhanced blood circulation, increased mobility, and faster healing times are commonly cited. For athletes, the therapy often means quicker return to training after injuries, while elderly patients appreciate its potential to alleviate chronic discomfort without relying heavily on medications. The therapy also shows promise in improving sleep quality, likely due to its effects on relaxation and circulation. While outcomes vary, these reported benefits underline its broad potential in supporting overall wellness. A patient testimonial once noted, “It felt as if my body remembered how to heal again,” capturing the essence of how the therapy resonates at a cellular level.
Reported Benefits of Pulsierende Signal Therapie
| Benefit Category | Reported Improvements | Typical Duration for Noticeable Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Pain Relief | Reduction in chronic joint and muscle discomfort | 3–6 sessions |
| Circulation | Improved blood flow, reduced swelling | 4–8 sessions |
| Tissue Repair | Accelerated healing of ligaments and bones | 6–10 sessions |
| Mobility | Increased range of motion, flexibility restoration | 5–9 sessions |
| Sleep & Relaxation | Better rest quality, reduced stress | 4–6 sessions |
Applications in Sports Medicine
Sports professionals often turn to pulsierende Signal Therapie as part of recovery strategies. Sprains, tendon injuries, and muscle tears can all benefit from the targeted stimulation this therapy provides. Athletes seek not only healing but also prevention of recurring injuries, and the therapy helps maintain tissue resilience. Professional trainers in Europe increasingly advocate for its use during off-season conditioning, ensuring muscles and joints remain healthy under strain. A sports physician once observed, “The beauty of this therapy lies in its ability to shorten downtime without risking long-term consequences.” Such endorsements highlight how performance-driven fields embrace the therapy for its efficiency and safety.
Use in Chronic Pain Management
Chronic pain remains one of the most persistent medical challenges, often leading to heavy reliance on painkillers. Pulsierende Signal Therapie offers an alternative by addressing the underlying dysfunction rather than simply masking discomfort. Patients with arthritis, fibromyalgia, or neuropathic pain often experience gradual improvement over consistent sessions. Unlike pharmacological solutions, the therapy does not carry risks of dependency or gastrointestinal complications. For many individuals, it becomes a sustainable tool for long-term management, enabling them to regain mobility and quality of life. Clinics often combine it with gentle exercise and dietary adjustments to create holistic care plans tailored to individual needs.
Comparison With Traditional Therapies
To better understand where pulsierende Signal Therapie stands, it is helpful to compare it with more conventional approaches such as physical therapy, medication, and surgery. While each has its role, pulsierende Signal Therapie often complements rather than replaces them.
Comparison of Therapies
| Therapy Type | Invasiveness | Recovery Time | Risk Factors | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulsierende Signal | Non-invasive | Short to moderate | Minimal side effects | Moderate |
| Physical Therapy | Non-invasive | Moderate | Fatigue, muscle soreness | Moderate |
| Medication | Non-invasive | Immediate relief | Dependency, organ strain | Varies widely |
| Surgery | Invasive | Long recovery | Infection, complications | High |
Safety Considerations and Limitations
While pulsierende Signal Therapie is generally safe, it is not recommended for everyone. Individuals with implanted pacemakers, certain types of metal implants, or severe cardiovascular conditions should avoid it. Pregnant women are often advised against undergoing this therapy until further safety research is available. Some patients report mild dizziness or temporary fatigue after sessions, though these effects are rare and typically resolve quickly. The main limitation lies in accessibility, as specialized equipment may not be available in all clinics, and insurance coverage varies widely across regions. Despite these caveats, the risk-to-benefit ratio remains favorable compared to more invasive procedures.
Patient Perspectives and Testimonials
Hearing directly from patients underscores the therapy’s value. One long-term arthritis patient described, “It gave me a kind of freedom that I had forgotten existed.” Another noted, “After knee surgery, I felt recovery would take forever, but with this therapy, I was walking comfortably in weeks.” Such accounts, while anecdotal, contribute to growing acceptance. They also highlight the psychological benefits of experiencing progress, as patients often regain hope and motivation for continued rehabilitation. The consistency of positive experiences encourages more practitioners to integrate the therapy into their treatment models.
Global Reach and Recognition
Though its development began in Europe, pulsierende Signal Therapie is gradually gaining recognition worldwide. Clinics in North America, Asia, and the Middle East are beginning to explore its potential, often branding it as part of advanced physiotherapy programs. Regulatory acceptance varies; some countries categorize it as a medical device therapy, while others classify it under complementary medicine. The global spread reflects a broader trend: patients increasingly demand non-invasive, technology-driven solutions that align with holistic health philosophies. Conferences on rehabilitation now frequently feature discussions on electromagnetic therapies, signaling that pulsierende Signal Therapie is steadily entering mainstream dialogue.
Future Directions and Innovations
Looking forward, researchers are exploring whether pulsierende Signal Therapie could extend beyond musculoskeletal applications. Preliminary studies suggest potential benefits in wound healing, nerve regeneration, and even mental health through modulation of brainwave activity. Device manufacturers are also working on portable models for home use, making the therapy more accessible. Artificial intelligence may play a role in customizing signal frequencies for individual patients, enhancing precision and outcomes. These innovations suggest a promising trajectory, where pulsierende Signal Therapie could evolve from a niche practice into a standard component of modern medicine.
Conclusion
Pulsierende Signal Therapie represents a bridge between natural biological rhythms and technological advancement. By harnessing pulsed electromagnetic signals, it supports healing, relieves pain, and restores function in ways that traditional medicine sometimes struggles to achieve alone. Its applications in sports recovery, chronic pain management, and rehabilitation underscore its versatility. Though limitations exist in accessibility and regulatory acceptance, its favorable safety profile and consistent patient testimonials make it an increasingly trusted option. As healthcare systems worldwide search for solutions that reduce invasiveness, costs, and long-term drug dependency, this therapy offers an innovative and promising pathway. As one researcher aptly stated, “Healing begins when cells remember their song, and pulsierende Signal Therapie helps them sing again.” With continuous research and growing global adoption, its future may redefine the very nature of rehabilitation and holistic wellness.
FAQs
Q1: What is pulsierende Signal Therapie used for?
It is primarily used for pain relief, orthopedic recovery, improved circulation, and chronic condition management without invasive procedures.
Q2: How many sessions are typically required to see results?
Most patients notice improvements after 3–6 sessions, though chronic conditions may require longer, consistent treatment plans.
Q3: Is pulsierende Signal Therapie safe for everyone?
It is generally safe but not recommended for individuals with pacemakers, certain implants, or during pregnancy.
Q4: Can athletes benefit from this therapy?
Yes, athletes often use it for faster injury recovery, prevention of recurring issues, and maintaining joint and muscle resilience.
Q5: Does health insurance cover pulsierende Signal Therapie?
Coverage varies depending on country and provider, with some insurance plans categorizing it under complementary or advanced physiotherapy.